Reducing Catheter Replacement Rates in Hemodialysis Patients: A Quality Improvement Initiative via Nephrologist, Surgeon, and Nursing Collaboration
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/wjnu1020Keywords:
Pediatric hemodialysis catheter, Quality improvement, Interdisciplinary collaboration, Catheter survivalAbstract
Background: Central venous catheters (CVCs) remain a common vascular access for hemodialysis (HD) initiation despite being known correlates of higher infection, hospitalization, and mortality rates. Poor coordination among dialysis nurses, nephrologists, and surgeons leads to delayed interventions for catheter dysfunction and results in unnecessary catheter replacement. The project aimed to reduce the rate of HD catheter replacement after initiation of HD below ≤ 10% through structured multidisciplinary practice.
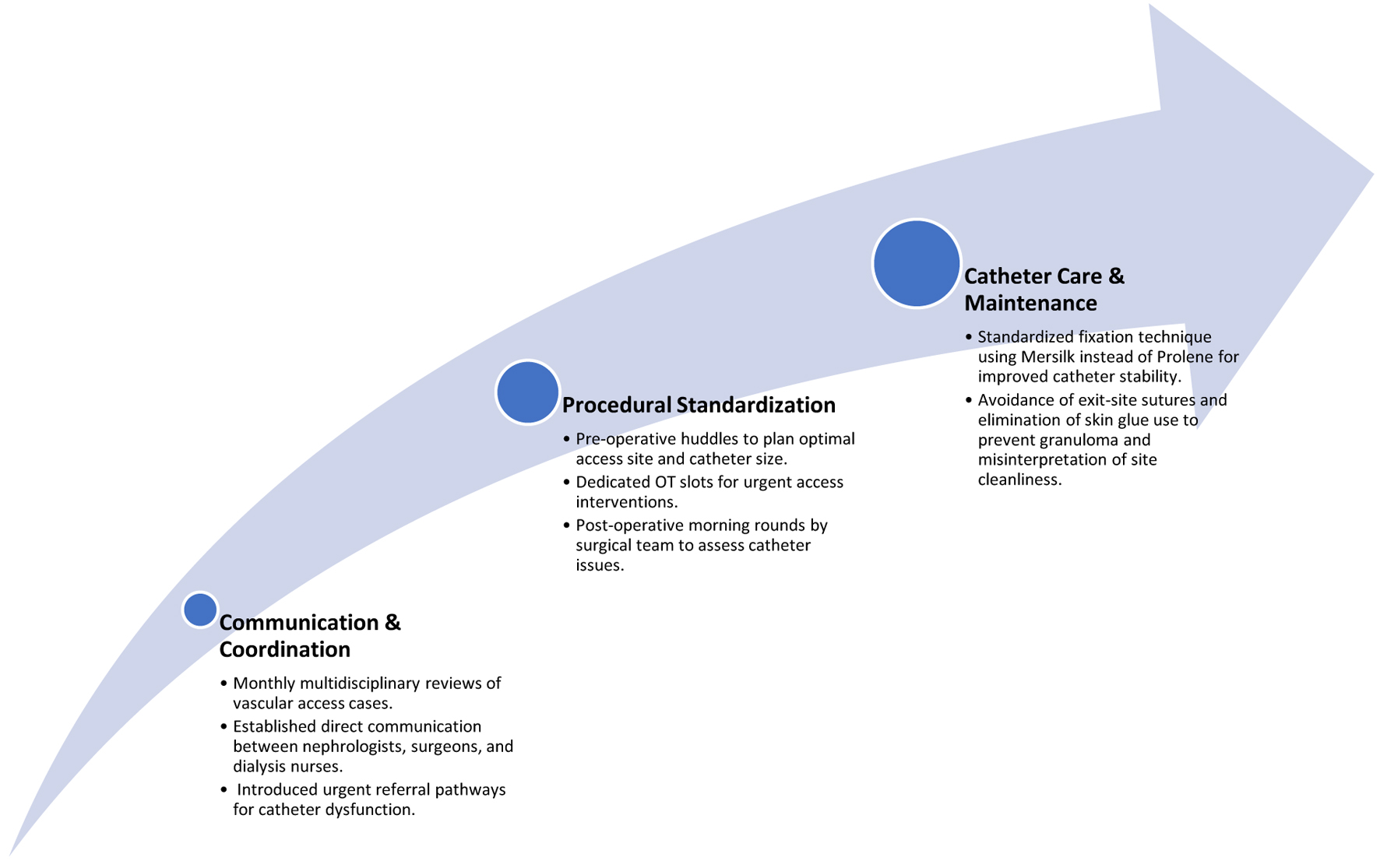
Methods: A multidisciplinary team is developed to establish open lines of communication between nephrologists, dialysis nurses, and the surgical team so that necessary interventions can be planned in real time through monthly vascular access rounds, pre-operative huddles, urgent operating theater (OT) slots, and standardization of the catheter insertion and fixation technique.
Results: The intervention yielded noteworthy improvements in vascular access outcomes. One-year catheter survival was increased from 27% (published benchmark) to 58%, and optimal maximum catheter lifespan was extended from 158 to 376 days with average life span being 196 days. Infection rates declined from 7% to 0%. Mechanical issues including kinking reduced from 9% to 2% and catheter fracture from 4% to 0%.
Conclusion: The organization of a multidisciplinary plan substantially improved HD catheter survival and decreased complications. Improved communication and coordinated care allowed improved patient safety, decreased catheter replacement, and increased healthcare efficiency.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





